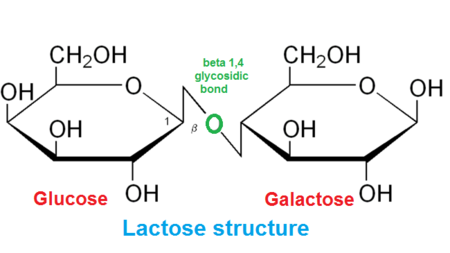
Q1. Name the sugar present in milk.
Answer:
Lactose sugar is present in the milk. There are two saccharide units present in the milk: glucose and galactose. Such oligosaccharides are called disaccharides.
Q2. Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid?
Answer:
Glucose is converted to gluconic acid by oxidation with bromine water and saccharic acid when oxidation is carried by conc. HNO3.
Q3. Which sugar is called invert sugar? Why is it called so?
Answer:
Sucrose is known as Invert Sugar.
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but, after hydrolysis, gives dextrorotatory glucose and laevorotatory fructose. Since the laevorotation of fructose (−92.4o) is more than the dextrorotation of glucose (+52.5o), the mixture is a laevorotatory. Thus, the hydrolysis of sucrose changes the sign of rotation from dextro (+) to laevo (−), and the product is named invert sugar.
Q4. Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. Explain.
Answer:
Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids due to the presence of both acidic (-COOH) and basic (-NH2) groups. In solution, the -COOH group can lose a proton, and an amine group can accept a proton, giving rise to a dipolar ion called the Zwitter ion.
Q5. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
Answer:
In glycylalanine, the carboxyl group of glycine combines with the amino group of alanine. 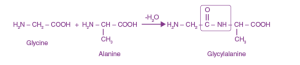
Q6. What are glycosidic linkages?
Answer:
Two molecules of monosaccharides are joined together by an oxide linkage formed by the loss of water molecules. A linkage between two monosaccharide units through an oxygen atom is called glycosidic linkage. It is present in disaccharides, trisaccharides and polysaccharides.