Class 12 chemistry important questions with answers are provided here for chapter 1 Solid State. These important questions are based on the CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 chemistry syllabus.
CBSE Previous Year Question
CBSE 2024 Solid State Chemistry Questions with Solutions
CBSE 2023 Solid State Chemistry PYQ Questions with Solutions
CBSE 2022
CBSE 2021
CBSE 2020
CBSE 2019
CBSE 2018
CBSE 2017
- A metallic element crystallises into a lattice having a pattern of AB AB … and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What type of structure is formed by this arrangement? (Comptt Delhi) 2017
Answer:
Tetrahedral void is formed in AB AB … pattern. The hexagonal close packing (HCP) is formed in this arrangement. - A metallic element crystallises into a lattice having a ABCABC … pattern and packing of spheres leaves out voids in the lattice. What type of structure is formed by this arrangement? (Comptt. Delhi) 2017
Answer:
Octahedral voids are formed in ABC ABC … pattern. The cubic close packing (CCP) is formed in this arrangement. - What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl? (Comptt. All India) 2017
Answer:
Schottky defect is shown by NaCl.
CBSE 2016
- What type of magnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction? (Delhi) 2016
Answer:
Ferromagnetism is shown by a substance if magnetic moments of domains are arranged in same direction. - Give an example each of a molecular solid and an ionic solid. (All India) 2016
Answer:
Molecular solid → Iodine (I2)
Ionic solid → Sodium chloride (NaCl)
CBSE 2015
- What is the formula of a compound in which the element Y forms ccp lattice and atoms of X occupy 1/3rd of tetrahedral voids? (Delhi) 2015
Answer:
Formula is X2Y3 - What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgCl? (Comptt. All India) 2015
Answer:
AgCl shows Frenkel defect.
CBSE 2014
- How many atoms per unit cell (z) are present in bcc unit cell? (Comptt. Delhi) 2014
Answer:
Number of atoms in a unit cell of a body centred cubic structure :
Contribution by 8 atoms on the corners
= (1/8) × 8 = 1
Contribution by the atom presents within the body = 1
∴ Total number of atoms present in the unit cell = 1 + 1 = 2 atoms - What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by NaCl? (Comptt. Delhi) 2014
Answer:
Schottky defect is shown by NaCl. - Write a distinguishing feature between a metallic solid and an ionic solid. (Comptt. Delhi) 2014
Answer:
The electrical conductivity in metallic substances is due to free electrons while in ionic substances the conductivity is due to presence of ions. - Why are crystalline solids anisotropic? (Comptt. All India) 2014
Answer:
Crystalline solids show different values of their some properties like electrical conductivity, refractive index, thermal expansion etc. in different directions. - What is meant by ‘antiferromagnetism’? (Comptt. All India) 2014
Answer:
Antiferromagnetism : These substances possess zero net magnetic moment because of presence of equal number of electrons with opposite spins. - Write a distinguishing feature of a metallic solid compared to an ionic solid. (Comptt. All India) 2014
Answer:
Metallic solid conducts electricity in solid state but ionic solids do so only in molten state or in solution or metals conduct electricity through electrons and ionic substances through ions. Metallic solids are malleable and ductile while ionic solids are hard and brittle.
CBSE 2013
- How many atoms constitute one unit cell of a face-centered cubic crystal? (Delhi) 2013
Answer:
4 atoms constitute one unit cell of a fee crystal. - What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by AgCl? (Delhi) 2013
Answer:
Frenkel defect is shown by AgCl. - What type of substances would make better Permanent Magnets: Ferromagnetic or Ferrimagnetic? (Delhi) 2013
Answer:
Ferromagnetic substances would make better I permanent magnets
Example : Fe, Co, Ni etc. - Calculate the number of atoms in a face centred cubic unit cell. (Comptt. Delhi) 2013
Answer:
In face centered cubic arrangement, number of lattice points are : 8 + 6.
∴ Lattice points per unit cell = 8×(1/8)+6×(1/2) = 4 - On heating a crystal of KCl in potassium vapour, the crystal starts exhibiting a violet colour. What is this due to? (Comptt. Delhi) 2013
Answer:
The Cl ions diffuse to the surface and combine with K(g) atoms which get ionized by losing electrons. These electrons are trapped in anions vacancies j and act as F-centre which imparts violet colour to the crystal.
Account for the following:
(i) Schottky defects lower the density of related solids.
(ii) Conductivity of silicon increases on doping it with phosphorus. (All India) 2013
Answer:
(i) Schottky defect produced due to missing of equal number of cation and anion from lattice as a result of which the density of the lattice solid decreases.
(ii) The conductivity of silicon increases due to negatively charged extra electron of doped pentavalent phosphorus.
Aluminium crystallizes in an fee structure. Atomic radius of the metal is 125 pm. What is the length of the side of the unit cell of the metal? (All India) 2013
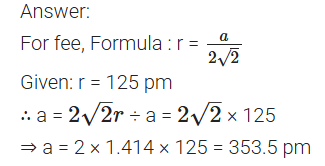
(a) What change occurs when AgCl is doped with CdCl2?
(b) What type of semiconductor is produced when silicon is doped with boron? (All India) 2013
Answer:
(a) Impurity defect of ionic solids is produced when AgCl is doped with CdCl2. Due to this defect vacancies are created that result in higher electrical conductivity of the solid.
(b) p-type semi-conductor is obtained when silicon is doped with boron.
If NaCl is doped with 10-3 mole percent SrCl2, what will be the concentration of cation vacancies? (NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1) (Comptt. All India) 2013

What is a semiconductor? Describe the tivo main types of semiconductors and contrast their conduction mechanism. (Comptt. All India) 2013
Answer:
Semiconductor : The solids which have intermediate conductivities between metals and non-metals i,e. between 10-6 to 104 π-1 m-31 are called semiconductors.
Example : Germanium and Silicon.
Main types of semiconductors are of two types :
(i) Intrinsic semiconductor : These are insulators at room temperature and become semiconductors when temperature is raised
(ii) Extrinsic semiconductor :
p-type semiconductor
n-type semiconductor
These are formed by dopping impurity of lower or higher group.
These are subdivided into two types :
• p-type semiconductor : When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group-13 elements like B, Al, Ga etc., the atom forms only 3 covalent bonds with the Si atom and 4th missing electron creates a hole which conducts electricity.
• n-type semiconductor : When a silicon crystal is doped with atoms of group-15 elements like P, As etc., then only four of the five valence electrons of each impurity atom, participate in 4 covalent bond formation and 5th e– conducts electricity.
A compound forms hep structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mol of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids? (Comptt. All India) 2013
Answer:
No. of atoms in the hep = 0.5 × 6.022 × 1023
= 3.011 × 1023
No. of octahedral voids
= No. of atoms in packing = 3.011 × 1023
No. of tetrahedral voids
= 2 × No. of atoms in packing
= 2 × 3.011 × 1023 = 6.022 × 1023
∴ Total no. of voids
= 3.011 × 1023 + 6.022 × 1023 = 9.033 × 1023
An element crystallizes in a structure having fee unit cell of an edge 200 pm. Calculate the density if 200 g of this element contains 24 × 1023 atoms. (Comptt. All India) 2013

CBSE 2012
- What is meant by ‘doping’ in a semiconductor? (Delhi) 2012
Answer:
Addition of a suitable impurity to a semiconductor to increase its conductivity is called doping. - Write a point of distinction between a metallic solid and an ionic solid other than metallic lustre. (Delhi) 2012
Answer:
Metallic solid conducts electricity in solid state but ionic solids do so only in molten state or in solution or metals conduct electricity through electrons and ionic substances through ions. Metallic solids are malleable and ductile while ionic solids are hard and brittle. - How may the conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor be increased? (All India) 2012
Answer:
The conductivity is increased by adding an appropriate amount of suitable impurity. This process is called as intrinsic doping. - What are n-type semiconductors? (All India) 2012
Answer:
n-type semiconductor : They are obtained by doping silicon with an element of group15, like P, As etc. - What type of stoichmetric defect is shown by AgBr and Agl ? (Comptt. All India) 2012
Answer:
AgBr shows both Frenkel defect and Schottky defect whereas Agl shows Frenkel defect. - What type of defect can arise when a solid is heated ? (Comptt. All India) 2012
Answer:
Vacancy defects can arise when a solid is heated. - Why does LiCl acquire pink colour when heated in Li vapours? (Comptt. All India) 2012
Answer:
This is due to metal excess defect due to anionic vacancies in which the anionic sites are occupied by unpaired electrons (F-centres).
The unit cell of an element of atomic mass 108 u and density 10.5 g cm-3 is a cube with edge length, 409 pm. Find the type of unit cell of the crystal. [Given : Avogadro’s constant = 6.023 × 1023 mol-1] (Comptt. Delhi) 2012
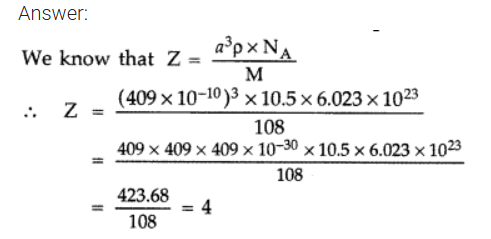
So it forms cubic- closed packed (ccp) lattice or fee structure.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples : Ferromagnetism and Ferrimagnetism (Comptt. Delhi) 2012
Answer:
Ferromagnetic solids : The solids which are strongly attracted by external magnetic field and do not lose their magnetism when the external field is removed are called ferromagnetic solids. The property, thus exhibited, is termed as ferromagnetism.
Example: Fe, Co and Ni show ferromagnetism at room temperature.
Ferrimagnetic solids : The solids which are expected to show large magnetism due to the presence of unpaired electrons but in fact have small net magnetic moment, are called ferrimagnetic solids.
Example : Fe3O4 and ferrites.
An element X crystallizes in f.c.c structure. 208 g of it has 4.2832 × 1024 atoms. Calculate the edge of the unit cell, if density of X is 7.2 g cm-3. (Comptt. Delhi) 2012
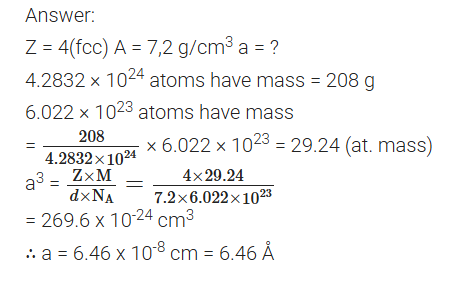
What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors. (Comptt. Delhi) 2012
Answer:
Semiconductor : The solid materials whose electrical conductivity lies between those of the typical metallic conductors and insulators are termed as semiconductors. The semiconductors possess conductivity in the range of 102 to 10-9 ohm-1 cm-1.
These are of two types :
(a) n-type semiconductors : Doping of higher group element impurity forms n-type semiconductors, e.g. when ‘As’ is doped in ‘Ge’.
(b) p-type semicondctors : Impurity of lower groups forms electron deficient bond in the structure. Electron deficiency develops to p-hole.
CBSE 2011
- ‘Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature.’ What does this statement mean? (Delhi) 2011
Answer:
It means that crystalline solids show different values of their some properties like electrical conductivity, refractive index, thermal expansion etc. in different directions. - Which stoichiometric defect in crystals increases the density of a solid? (Delhi) 2011
Answer:
Interstitial defect in crystals increases the density of a solid.
Explain how you can determine the atomic mass of an unknown metal if you know its mass density and the dimensions of unit cell of its crystal. (All India) 2011

Define the following terms in relation to crystalline solids :
(i) Unit cell (ii) Coordination number Give one example in each case. (All India) 2011
Answer:
(i) Unit cell : The smallest three dimensional portion of a complete space lattice which when repeated over and again in different directions produces the complete space lattice is called the unit cell.
Example: Cubic unit cell, Hexagonal unit cell etc.
(ii) Coordination number : The number of nearest spheres with which a particular sphere is in contact is called co-ordination number.
Example : Co-ordination number of hexagonal (hep) structures is 12.
CBSE 2010
- Which point defect in crystals of a solid decreases the density of the solid? (Delhi) 2010
Answer:
Schottky defect. - What type of interactions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid? (All India) 2010
Answer:
Dipole-dipole forces of attractions hold the molecules together in a polar molecular solid. - What type of semiconductor is obtained when silicon is doped with arsenic? (All India) 2010
Answer:
n-type semiconductor. - Write a distinguishing feature of metallic solids. (All India) 2010
Answer:
Metallic solids possess high electrical and thermal conductivity due to presence of free electrons.
CBSE 2009
- Which point defect in crystals does not alter the density of the relevant solid? (Delhi) 2009
Answer:
Frenkel defect. - How do metallic and ionic substances differ in conducting electricity? (All India) 2009
Answer:
The electrical conductivity in metallic substances is due to free electrons while in ionic substances the conductivity is due to presence of ions. - What is the number of atoms in a unit cell of a face-centred cubic crystal? (All India) 2009
Answer:
The number of atoms in a unit cell of fcc-crysta! is 4 atoms.







