This page provides a thorough outline of the WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus, Questions & Notes for 2025. The students need to review the Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus for the West Bengal Board of Secondary Education in 2025 and intensify their studies.
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Semester 3
| Semester 3 Class Start | 07.04.2025 |
| Pre Semester 3 Exam | 15.09.2025 |
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus Semester 3
| Unit Name | Contact Hours (69 Class) | Marks (MCQs) |
| Unit-1: Liquid State | 16 (15 Class) | 08 |
| Unit-2: p-Block Elements | 18 (16 Class) | 08 |
| Unit-3: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 10 (10 Class) | 05 |
| Unit-4: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | 10 (12 Class) | 05 |
| Unit-5: Biomolecules | 08 (10 Class) | 05 |
| Unit-6: Polymers | 08 (06 Class) | 04 |
Unit-1: Liquid State
Introduction, Solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, Vapour pressure and Raoult’s law. Colligative properties; relative lowering of vapour pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure. Determination of molecular mass using colligative properties. Abnormal molecular mass, van’t Hoff factor and calculations involving it.
Colloidal solution, the difference between true solutions, colloids and suspensions; lyophilic, lyophobic, multi-molecular colloids; properties of colloids; Tyndal effect, Brownian movement, electrophoresis, coagulation, emulsions and types of emulsions
Read More:
- Liquid State Topic Wise Important Questions- PYQ & DPP 2025
- [Bengali] Liquid State Online Mock Test -1
- [Bengali] Liquid State Online Mock Test -2
- [Bengali] Liquid State Online Mock Test -3
- [Bengali] Liquid State Online Mock Test -4
Unit-2: p-Block Elements
- Group 15 elements: general introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states, Structure and reaction of NH3, HNO3, NCl3, oxides of nitrogen (structure only); Phosphorus – allotropic forms( White and Red), preparation and properties of phosphine, phosphorus halides (PCl3, PCl5) and oxoacids (elementary idea only)
- Group 16 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, oxidation states; Oxygen: classification of oxides. Preparation and properties of Ozone. Sulphur: allotropic forms (rhombic and monoclinic). Properties and uses of oxides, oxoacids and peracids of sulphur.
- Group 17 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, oxidation states, occurrence, trends in physical and chemical properties ;Compounds of halogen; preparation, structure and uses of oxides, oxoacids of halogens, interhalogen compounds. Elementary idea of pseudohalogens and polyhalides.
- Group 18 elements: General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence, uses of noble gases. Preparation, structure and chemical reactions of XeO2, XeO3, XeF2, XeF4, XeF6, XeOF2.
Read More:
Unit-3: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C-X bond, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of substitution reactions. Stability of carbocations. R/S and D/L configurations Uses and environmental effects of – dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons.
- Haloarenes: Nature of C-X bond, substitution reaction (directive influence of halogen for monosubstituted compounds only), stability of carbocations, R/S and D/L configurations. Uses and environmental effects of DDT.
Read More:
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Topic Wise Questions: PYQ & DPP 2025
- [Bengali] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Online Mock Test 20 MCQ-1
- [Bengali] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Online Mock Test 20 MCQ-2
- [Bengali] Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Online Mock Test 20 MCQ-3
Unit-4: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (primary alcohols only); identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols; mechanism of dehydration, uses of methanol and ethanol.
- Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reaction, uses of phenol.
- Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses
Read More:
Unit-5: Biomolecules
- Carbohydrates: Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), D/L configuration, oligosaccharides (sucrose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose)
- Proteins: Elementary idea of α-amino acids, peptide bonds, polypeptides, structure of proteins (primary structure only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes.
- Nucleic Acids: DNA & RNA (introduction and basic concept)
Read More:
Unit-6: Polymers
Classification- (natural and synthetic), methods of polymerization (addition and condensation), copolymerization. Some important polymers; like polythene, nylon, polyesters, bakelite, and rubber. Biodegradable and nonbiodegradable polymers.
Read More:
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Semester 4
| Semester 4 Class Start | 02.10.2025 |
| Pre Semester 4 Exam | 02.02.2026 |
| Semester 4 Final Exam | March First Week |
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus Semester 4
| Unit Name | Contact Hours (63 Class) | Marks |
| Unit-1: Electrochemistry | 08 (08 Class) | 05 (2+3) |
| Unit-2: Chemical Kinetics | 10 (10 Class) | 07 (2+5) |
| Unit-3: d- and f -Block Elements | 10 (08 Class) | 05 (3+3) |
| Unit-4: Coordination Compounds | 08 (10 Class) | 05 (2+3) |
| Unit-5: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | 10 (14 Class) | 05 (5) |
| Unit-6: Amines | 14 (12 Class) | 07 (2+2+3) |
Unit-1: Electrochemistry
Redox reactions, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity, variation of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch’s law, electrolysis and laws of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell – electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells, emf of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, relation between Gibbs energy change and emf of a cell, fuel cells, Li-ion battery.
Unit-2: Chemical Kinetics
Rate of a reaction (average and instantaneous), factors affecting rate of reactions- concentration, temperature and catalyst. Order and molecularity of a reaction; rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first order reactions); the concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment) activation energy, Arrhenius equation
Catalysis, homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis, enzyme catalysis.
Unit-3: d- and f -Block Elements
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first-row transition metals – ionic radii, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, colour, catalytic property, magnetic property. Preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
Lanthanoid: Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity, lanthanoid contraction and its consequences, uses.
Actinoids: Electronic configuration, oxidation states, comparison with lanthanoids, uses.
Unit-4: Coordination Compounds
Introduction, ligands, classification of ligands based on denticity and field intensity, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shape, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds, EAN rule, Bonding (Werner’s theory, VBT and CFT), CFSE, structural-isomerism and stereoisomerism, importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological systems)
Unit-5: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes; uses.
Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses
Unit-6: Amines
Nitro compounds: General methods of preparation and reduction reactions. Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Cyanides and Isocyanides – Nomenclature, structure, methods of preparation, chemical reactions (hydrolysis and reduction reactions only).
Diazonium salts: Preparations, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry
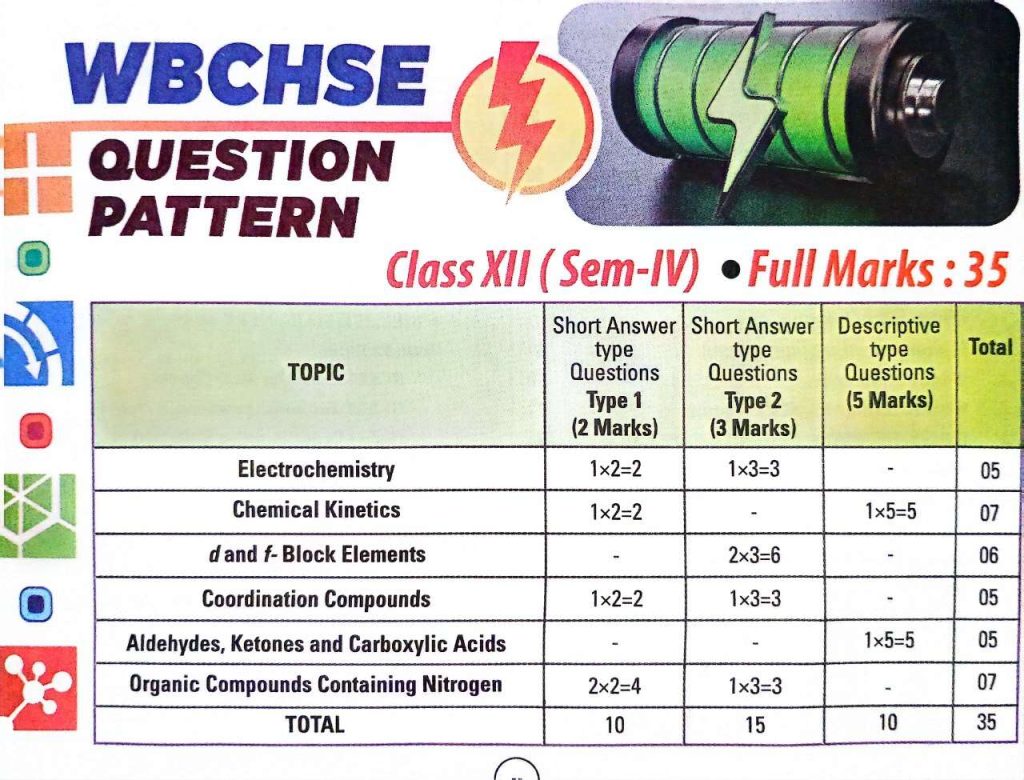
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Semester 4 Previous Year Question Paper
| Electrochemistry WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
| Chemical Kinetics WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
| d- and f -Block Elements WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
| Coordination Compounds WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
| Carbonyl Compound WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
| Amines WBCHSE Class 12 Previous Year Question Paper |
Here we are providing the WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Model Paper Solution, which will help in examining the performance of students in Chemistry.
By working on the weak areas, they can improve their performance in the board exam.
Here at Studenthelp, you can get Chemistry Chapter wise NEET previous year question papers.
WBCHSE Class 12 Chemistry Semester 4 Notes
Read More:








